Cannabis Deficiencies: Symptoms and Solutions

Cannabis deficiencies are a common issue that many growers face when cultivating their plants. These deficiencies occur when the plant is lacking essential nutrients, which can cause a variety of problems, including stunted growth, discolored leaves, reduced yields, and even death. In this article, we will discuss the most common cannabis deficiencies, their causes, lack of nutrients, symptoms, and how to identify and treat them to ensure that your plants grow healthy and strong.
Every experienced grower knows that it is vital to monitor a plant's nutrient levels and address any flaws promptly to ensure proper growth and development. One way to identify and treat these scarcities is to refer to a weed plant deficiency chart.
The type of fertilizers and the growing medium used can also have a significant impact on the growth of cannabis plants. While fertilizers can provide essential nutrients, overuse can lead to nutrient burn, which causes damage to the plant. It's essential to keep an eye on the nutrient levels in the soil to determine when to stop using fertilizers. Additionally, choosing the right growing medium can also affect the plant's growth. Some popular ones for weed include soil, coco coir, and hydroponics. Each medium has its advantages and disadvantages, and it's important to choose the one that works best for the seedlings and growing conditions.
Read Also: How to Plant Marijuana Seeds: Secrets and Recommendations
pH for Cannabis: The Risks and Consequences
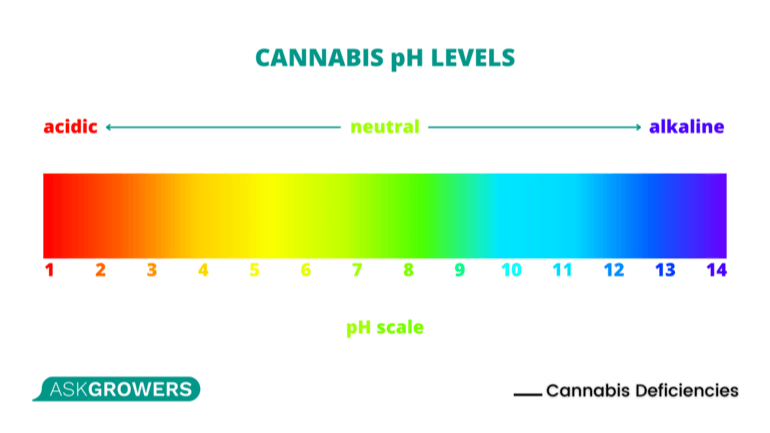
When cultivating cannabis, it is essential to take into account the pH level. The optimal pH level for cannabis plants in the hydroponic system is between 6.0 and 7.0. However, the exact pH level will vary depending on the specific strain, grow mediums for weed, and nutrient regimen being used.
The healthy growth of plants is dependent on the maintenance of this factor. If the pH level is too low or acidic, it can lead to nutrient deficiencies, as some essential elements become unavailable to the plant. Signs of low pH in weed plants include yellowing of the leaves, stunted growth, and reduced yields. In severe cases, the leaves may even turn brown and die.
On the other hand, if the pH level is too high or alkaline, it can also lead to nutrient deficiencies as well as toxicities. Signs of high pH in weed plants include slow growth, wilting, and browning on the leaves.
It is important to regularly test and adjust the pH level of the growing medium to ensure optimal plant growth. pH levels can be adjusted using pH-up or pH-down solutions or by using natural methods such as adding organic matter to the soil.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take to Grow Marijuana: Stages of Growth
The Role of Mobile and Immobile Nutrients in Plant Health
Mobile nutrients are those that can be easily translocated within the plant, meaning they can be moved from older to younger leaves or from roots to leaves. Some examples of mobile marijuana nutrients include the following:
-
Chlorine (Cl)
-
Nickel (Ni)
-
Nitrogen (N)
-
Phosphorus (P)
-
Potassium (K)
-
Magnesium (Mg)
-
Molybdenum (Mo)
Immobile nutrients are those that cannot be easily translocated within the plant. They are primarily found in new growth and cannot be moved to older leaves or other parts of the plant. Examples of immobile nutrients in marijuana plants are the following:
-
Boron (B)
-
Calcium (Ca)
-
Copper (Cu)
-
Iron (Fe)
-
Manganese (Mg)
-
Sulphur (S)
-
Zinc (Zn)
One way to overcome the deficiencies of mobile and immobile nutrients in plants is by carefully administering the deficient nutrients to the growing medium in a controlled manner. To prevent overfeeding and the risk of salt buildup leading to complete nutrient lockout, it's recommended to slowly increase the dosage of the deficient nutrients or gradually switch to a more suitable fertilizer for your plant.
If your plants are experiencing deficiencies of mobile nutrients, you might want to try foliar fertilization to address the issue more rapidly. However, it's worth noting that this approach may not be as effective in treating nitrogen deficiencies since the affected plant will usually require a higher amount than what can be provided through a foliar spray.
Read Also: Is Growing CBD-Rich Marijuana Different From Growing High-THC Cannabis?
Weed Nutrient Deficiency: Symptoms and Solutions
Unfortunately, even with the best care and attention, nutrient deficiencies can occur, leading to stunted growth, weak stems, and poor yields. Understanding the symptoms of nutrient deficiencies and how to treat them is crucial for cultivators who plant marijuana seeds. Further, we will explore the most common nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants, their symptoms, and effective ways to remedy them.
Potassium (K)
Potassium’s primary function is to facilitate the movement of vital nutrients, water, and carbohydrates throughout the plant tissue, which helps to promote growth and development. When cannabis plants have sufficient potassium, they can effectively synthesize proteins and amino acids delivered by nitrogen, which enhances their ability to withstand biotic and abiotic stresses such as pests, drought, and frost. Additionally, potassium strengthens plant tissue and root systems, activates growth-promoting enzymes, and improves plant morphology, leading to larger, denser, and more potent cannabis buds.
| Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency | Treating Measures |
|---|---|
| Leaves curl | Adjust the soil's pH to the appropriate range and provide potassium-rich fertilizers |
| Yellowing of leaves | Apply potassium-rich fertilizers |
| Poor growth and development | Use a potassium supplement to replenish the depleted nutrients |
| Nutrient lockout | Flush the soil with pH-balanced water to remove excess salts and adjust the pH to optimal levels |
Magnesium (Mg)
Magnesium plays a vital role in the process of photosynthesis, as it is necessary for the absorption and conversion of light into energy by the leaves. Magnesium deficiency can also hinder the development of robust root systems and healthy flowers in cannabis plants. This can be a significant setback for both the plants and the growers, as it can lead to reduced yields and compromised quality of the harvest.
| Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency | Treating Measures |
|---|---|
| Yellowing of leaves, starting from the bottom | Apply a magnesium-rich fertilizer to the soil |
| Leaf curling or cupping | Apply magnesium sulfate (Epsom salt) through foliar spray or soil drench |
| Cannabis brown spots on leaves | Use a magnesium supplement to replenish the depleted nutrients |
| Slow growth and stunted development | Use a fertilizer containing magnesium, and adjust the pH of the soil to optimal levels |
Calcium (Ca)
Calcium fortifies the cell walls and membranes of cannabis plants. This enhances the plant's natural defenses against pests and diseases and promotes the development of a sturdy and robust structure. In the absence of proper calcium, the growth of plants can be stunted, and the leaves and stems may become weak and vulnerable to damage. Furthermore, calcium facilitates the absorption of essential nutrients and water from the soil, thereby improving the overall nutrient uptake of the plant. Additionally, Calcium promotes root development, which is essential for anchoring the plant in the soil and facilitating nutrient absorption.
| Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency | Treating Measures |
|---|---|
| Brittle and weak stems | Add calcium-rich amendments to the soil, such as dolomite lime or gypsum |
| Yellowing of new leaves | Use calcium-rich fertilizers, such as bone meal or fish bone meal |
| Cannabis leaf curl | Maintain proper pH levels of soil and check it weekly |
| Leaf tip burn | Ensure proper airflow |
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus is involved in the formation of nucleic acids and enzymes, which are important components of plant cells. It helps to transfer energy within the plant by participating in the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary energy currency of cells. Additionally, phosphorus plays a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis by facilitating the transfer of energy from light to chemical energy.
Lacking sufficient phosphorus, marijuana plant deficiencies will display symptoms such as slow growth, small and underdeveloped leaves, and a reduction in overall plant size.
| Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency | Treating Measures |
|---|---|
| Dark green leaves with red or purple stems | Adjust the pH level of the soil to the optimal range |
| Small and underdeveloped buds | Reduce the amount of nitrogen in the soil |
| Older leaves turning yellow, brown, or bronze | Adjust adequate light and proper watering to promote nutrient uptake |
| Stunted or weak stems | Use a root stimulant to promote root growth |
Iron (Fe)
Iron plays a crucial role in photosynthesis and respiration. It is a key component of several enzymes and proteins that are involved in electron transport, which is necessary for energy production in the plant. It also helps the plant produce chlorophyll, the pigment that gives plants their green color and enables them to absorb light energy for photosynthesis. Without sufficient iron, the seeding can suffer from a condition called iron chlorosis, where the leaves of pot plants turn yellow with green veins.
| Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency | Treating Measures |
|---|---|
| Yellowing of the leaves towards the center | Apply iron-rich fertilizers or supplements, such as iron chelates or iron sulfate |
| Leaves develop brown or bronze-colored spots | Adjust the pH of the soil to ensure proper iron uptake |
| Slow growth and stunted development | Make sure not to overwater plants |
| Reduction in the number of buds or flowering sites | Increase the amount of phosphorus and potassium in the plant's diet |
Read Also: The Ultimate Guide to Growing Marijuana Indoors
Zinc (Zn)
Zinc is one of the essential cannabis nutrients that play a critical role in various physiological and biochemical processes of plants. It is involved in the production of auxins, a type of plant hormone responsible for regulating plant growth and development. Zinc also plays a crucial role in the synthesis of chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis. In addition, zinc helps the plant to resist stress by producing stress-responsive proteins and enzymes. It is also required for the proper functioning of enzymes involved in DNA synthesis and cell division.
| Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency | Treating Measures |
|---|---|
| Stunted plant growth | Adjust soil pH to promote zinc uptake |
| Delayed maturity of buds | Use foliar sprays of zinc supplements |
| Leaf deformation | Add zinc to irrigation water |
Copper (Cu)
Copper is a component of many enzymes involved in photosynthesis, respiration, and the production of hormones. It helps to activate enzymes that facilitate plant growth and development, including the synthesis of chlorophyll. In addition, copper aids in the formation of lignin, which strengthens cell walls and supports plant structure. A lack of copper in plants can result in stunted growth and severe cannabis leaf problems such as necrosis (tissue death).
| Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency | Treating Measures |
|---|---|
| Leaf tips become twisted and dark and become rigid | Adjust soil pH to make it more acidic |
| Stems turn brown or black | Increase the frequency of feeding with copper-rich nutrients |
| Reduced growth | Use copper fungicides to protect against root rot or other fungal diseases |
| Chlorosis or yellowing between leaf veins | Consider adding chelated copper to your nutrient solution |
CalMag
CalMag is an essential nutrient for cannabis plants that contains calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) in a balanced ratio. It plays a vital role in preventing nutrient deficiencies, as it can improve the uptake of other nutrients like nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus. It also helps to prevent plant stress caused by environmental factors such as high humidity and low temperatures. A deficiency of CalMag can arise due to the use of heavy phosphorus-based fertilizers, subjecting the garden soil to RO-treated water or if the soil is sandy or coarse.
| Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency | Treating Measures |
|---|---|
| Brown or black spots on leaves | Increase calcium and magnesium in the nutrient solution |
| Curling or cupping of leaves | Adjust nutrient solution to the proper EC level |
| Weak stems | Ensure proper drainage and aeration |
| Slow development of buds or flowers | Apply foliar spray with CalMag supplement |
Read Also: How to Sex a Marijuana Plant: Guide for Beginning Growers
Conclusion
Each mineral plays a vital role in the growth and development of cannabis plants. By understanding the reasons behind the nutrient deficiencies, growers can take appropriate measures to prevent and address the issues, ensuring their plants remain healthy and productive. With proper care and attention to the plant’s needs, growers can avoid common deficiencies and produce a bountiful harvest of high-quality buds.

 Growing
Growing



.png)


 (1).png)
.jpg)





Be the first and share your opinion
Write a Review