Exploring CBD: From Plant to Potential Health Benefits

CBD (or cannabidiol), which is a chemical compound of the cannabis plant. This phytocannabinoid was discovered in 1940. It is one of 113 cannabinoids, unlike delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), it does not have psychoactive properties.
Medical Research
The therapeutical effects of CBD (hemp oil) are being actively tested by medical scientists around the world.
Early studies focused on the role of the brain’s cannabinoid receptors in processing CBD, as well as its influence on the production of dopamine. Recently, doctors have launched some studies and clinical trials to find other potential uses for CBD. These studies include exploring the role of cannabidiol for Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and psoriasis treatment.
The critical review report of the World’s Health Organization asserts that CBD can be an effective remedy for epilepsy since cannabidiol has been proven to have anti-seizure properties. Also, a study conducted by Yeshurun demonstrated the mechanism of action of CBD for transplant acceptance while McGuire’s research showed that CBD can reduce some of the symptoms of schizophrenia, probably because endocannabinoids bind D2 receptors.
What Does CBD Do?
Let’s look attentively at the benefits of CBD consumption for our bodies. Studies made it clear that CBD may relieve chronic arthritis pain by reducing inflammation. Also, people suffering from multiple sclerosis who used Sativex, which is an oral spray with CBD, experienced improvements in motor ability, and muscle spasms during the study. This remedy reduced spasms in 75% of people who had muscle spasticity insensible to medications. Therefore, it is approved in some countries to treat pain caused by multiple sclerosis.

Sativex is helpful for severe epilepsy too. According to another study, 214 patients took 0.9–2.3 grams of cannabidiol oil per pound of body weight, and seizures reduced on average by 36.5%.
Moreover, CBD oil demonstrates the potential for both depression and anxiety treatment. A Brazilian study showed that taking a 300-mg dose of CBD can significantly reduce anxiety levels. Researchers have also proven that it can be used to safely medicate insomnia in kids with post-traumatic stress disorder.
Another significant medical benefit of CBD is that it can alleviate symptoms related to cancer treatment. Since it might be associated with nausea, vomiting, and painful sensation, CBD may be used to avoid these side effects. A study of patients undergoing chemotherapy found that medicine containing CBD diminished nausea and vomiting better than ordinary treatment alone.
Based on recent research, cannabidiol might be used as a remedy against acne because of its anti-inflammatory effects. Besides, it prevents secreting cells from releasing excessive sebum, according to one study.
Read Also: CBD for Sleep and Insomnia
Endocannabinoid System and CBD
We all have the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in our bodies that is partially responsible for the regulation of numerous physiological functions, including sleep, motor control, memory, appetite, mood, immune system response, and pain management.

The ECS consists of three main components:
- endocannabinoids or endogenous cannabinoids that are similar to cannabinoids, but produced in the body;
- receptors;
- enzymes that are accountable for breaking down components of the endocannabinoid.
Let’s consider each of them in detail.
There are two main endocannabinoids known to experts so far: anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). They help the body to keep its functions running smoothly.
These endocannabinoids bind to CB1/CB2 receptor cells in the central/peripheral nervous system respectively, signaling that the ECS needs to act.
Once they have performed their function, enzymes (fatty acid amide hydrolase or monoacylglycerol acid lipase) break down endocannabinoids.
Scientists aren’t completely assured how CBD interacts with the ECS, but they believe that it inhibits the fatty acid amide hydrolase and thus, prevents endocannabinoid compounds from being broken down. This way, endocannabinoids can have more of an effect on the body.
Serotonin Receptors
CBD has the capability to affect the brain’s receptors for serotonin, one of the neurotransmitters that are responsible for regulating mood and social behavior.
Scientists of the University of San Paulo in Brazil together with King’s College in London revealed that CBD can mimic serotonin and activate the 5-HT1A (hydroxytryptamine) serotonin receptors, which leads to both antidepressant and anti-anxiety effects.
TRPV1 (Vanilloid) Receptors
Vanilloid receptors or TRPV1 receptors are located throughout the body where they detect temperature and mediate pain perception. When one has inflammation or injury, the sensitivity of vanilloid receptors can be increased. Hence, an individual experiences painful sensations. CBD can bind to TRPV1 receptors and desensitize them. That is why it can be used for pain relief.
Orphan Receptors
CBD can be a deactivator of some receptors too. For instance, it functions as an antagonist that blocks GPR55 receptors or orphan receptors. They are called so because scientists still don’t know if they belong to a larger family of receptors.
GPR55 is involved in the regulation of blood pressure and bone density. High GPR55 receptor activity increases the risk of osteoporosis.
Nuclear Receptors
Not all receptors are located outside of the cells, some of them exist within it. Since they are found on the cell’s nucleus, they are called nuclear or peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor cells. Their main function is to help regulate metabolism by lowering blood glucose levels and improving insulin sensitivity. Hence, people suffering from diabetes may benefit from CBD activating nuclear receptors.
Benefits and Side Effects
CBD can affect the body in numerous positive ways since it has the potential to help with the treatment of epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, anxiety, depression, PTSD, chronic pain, and inflammation.
Even though CBD is mostly well tolerated and not associated with abuse potential, it might cause negative reactions in some people. Some side effects of CBD may include fluctuations in appetite and weight, fatigue, and diarrhea. Besides, you have to avoid potentially harmful interactions with other medications. Therefore, it’s important to consult your doctor before you decide to use this remedy.
How to Use CBD
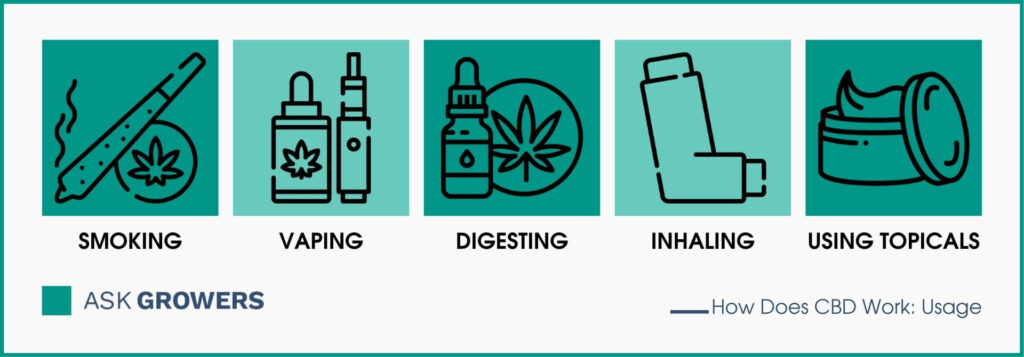
CBD can be used in different ways, which include:
- smoking
- vaping
- digesting
- inhaling
- using topicals.
The effects CBD can have on the brain vary significantly from one person to another. Thus, you should always ask your doctor about the preferred way of CBD consumption.
Final Thoughts
Although there are still a lot of unanswered questions to be researched, CBD is currently considered a potential treatment for various conditions mentioned above. The statistics show that CBD is mostly used by Americans for pain relief, namely in 64% of cases. Among people who use this remedy, 49% of them do it to reduce anxiety, and 42% - to beat insomnia.
Hemp CBD can affect the brain in different ways, but it has the strongest influence on the endocannabinoid and serotonin systems. In general, it is an exceptional natural remedy that works well for overall health improvement.

 Guides
Guides
 CBD
CBD

.png)
.png)



 (1).png)

.jpg)





Be the first and share your opinion
Write a Review