Cannabis Mutations: Definition and Process Overview
Cannabis is the name of the group of three plants that have psychoactive properties. Cannabis, also known as Cannabis sativa L., Cannabis Indica, and Cannabis Ruderalis, is used for recreational, growing, and medical purposes, depending on several factors. Healthy seedlings of the plant have to be short with thick vegetation. Their leaves should be vibrant green in color. In order to keep the plant healthy, growers should maintain proper conditions, ensuring the environment is clean and free of excess moisture.
Although the environment where the plant grows plays a key role, genetic mutations can occur. They happen when cells reproduce, whether it is within one plant or when two plants create a new one. When cell reproduction causes mutation, the results are bad or negligible. Mutation can be bad or good during the creation of the new weed because this is the process of evolution.
Thanks to the nature of recessive alleles, most types of cannabis leaf mutations go by totally unnoticed. In terms of weed, many plants will have a genetic code containing some sort of mutation, though in most cases, they never find themselves expressed. However, there is also a case where two weed plants will breed, and the recessive alleles will become dominant, which results in a mutant phenotype. Since some growers wonder what are sugar leaves on a weed plant or why a plant has three leaves, we are going to describe the most popular mutations below.
Weed Mutations List & Everything You Need to Know
There are several types of mutations you should know, and each derives into several subcategories.
Cannabis Leaf Mutations
Cannabis leaves are the most visually recognizable and known part of the weed. Mutations of weed leaves can be easily noticed. This mutation divides into the following categories:
- DUCKFOOT CANNABIS
- AUSTRALIAN BASTARD CANNABIS
- VARIEGATION AND ALBINISM
- TWO-TONED LEAVES
Cannabis Flower Mutations
Just like cannabis leaves, flowers can also mutate into unusual and surprising forms. Mutations of cannabis flowers are also pretty recognizable.
- FOXTAIL BUDS
- LEAF BUDS
- POLYPLOIDY
- STRINGY BUDS
Cannabis Plant Mutations
Some types of mutations can affect the entire plant or how it grows. These cause the plant to look completely different.
- WHORLED PHYLLOTAXY (THREE-LEAF SEEDLINGS)
- VINE CANNABIS
- CREEPER
- TWIN SEEDLINGS
- SELF-TOPPING
Read Also: F1, F2, S1 Hybrid Marijuana Seeds: Guide for Beginners
Let's explore the most common types of cannabis mutations:
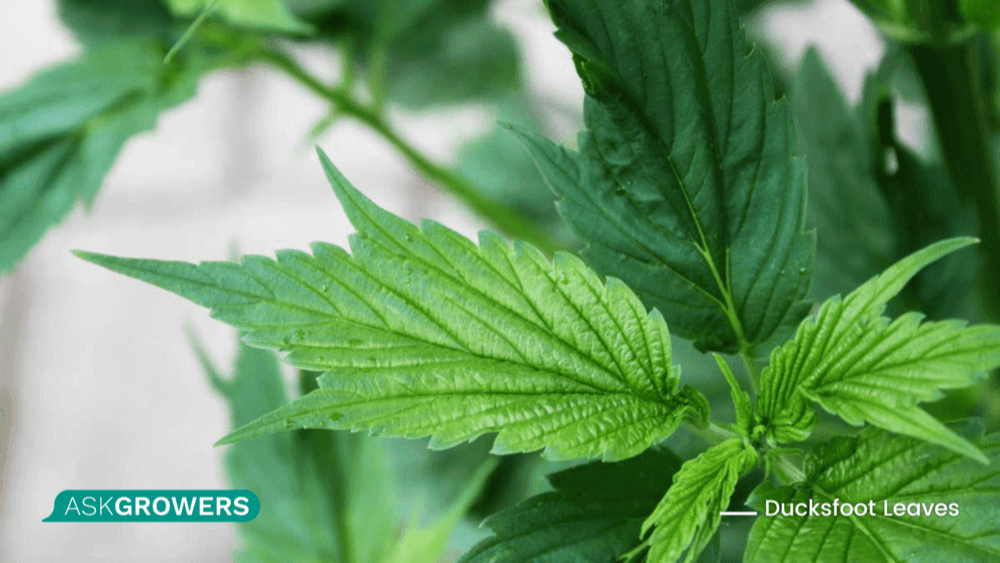
Ducksfoot Leaves
Ducksfoot, also known as webbed cannabis leaves, is one of the most popular cannabis mutations that causes the normally separated fingers on the plant to melt together. The leaf shape you get with that mutation resembles the shape of a duck footprint, which gave the mutation its name. This type of mutation mostly appears in outdoor cannabis growers or guerrilla growers.
The different-looking leaves are just the start. Most ducksfoot weeds will grow into Sativa plants. This cannabis is popular among growers that cultivate the plant in countries where it is not legalized yet, thanks to its "normal" appearance. This weed can also produce purple buds if the temperature is cold enough.

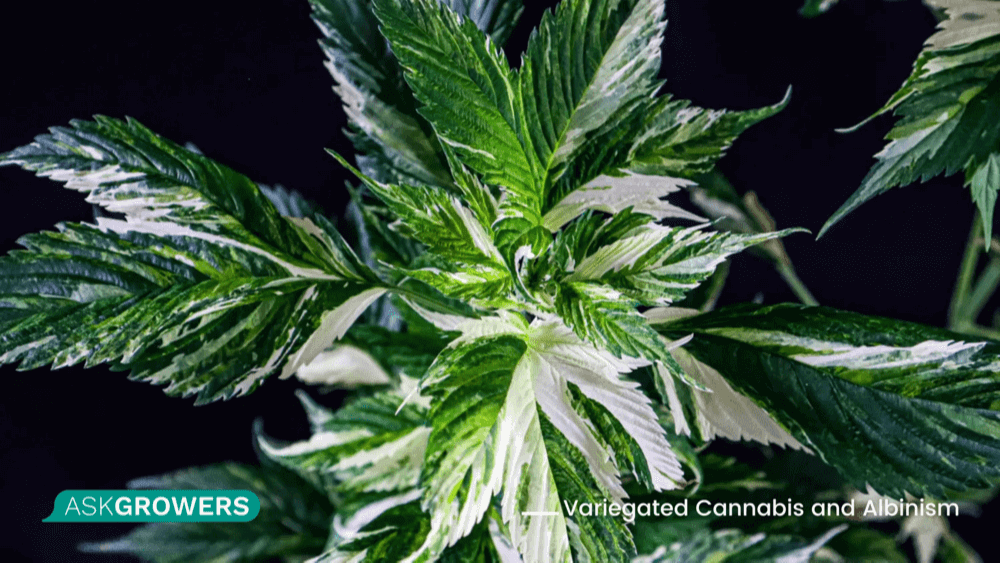
Variegated Cannabis and Albinism
As a grower or recreational smoker, you should know that marijuana can be in different colors. The color usually depends on the Indica or Sativa genetics of the strain and growing conditions. However, cannabis can also be albino. That means the plant itself can be without pigmentation, and growers can see a white cannabis leaf.
The technical term for this mutation is variegation. This mutation is primarily caused by a genetic malfunction of the genes responsible for chlorophyll. Although this phenomenon is mostly true for the entire plant, growers can notice these features isolated to certain parts of the plant.
For instance, albino weed may only have colorless buds. While these plants are beautiful, they aren't very useful and efficient for bud production. Weed with such a mutation also tends to die quickly since it cannot synthesize light due to a lack of chlorophyll, which is an essential part of plant growth and health.

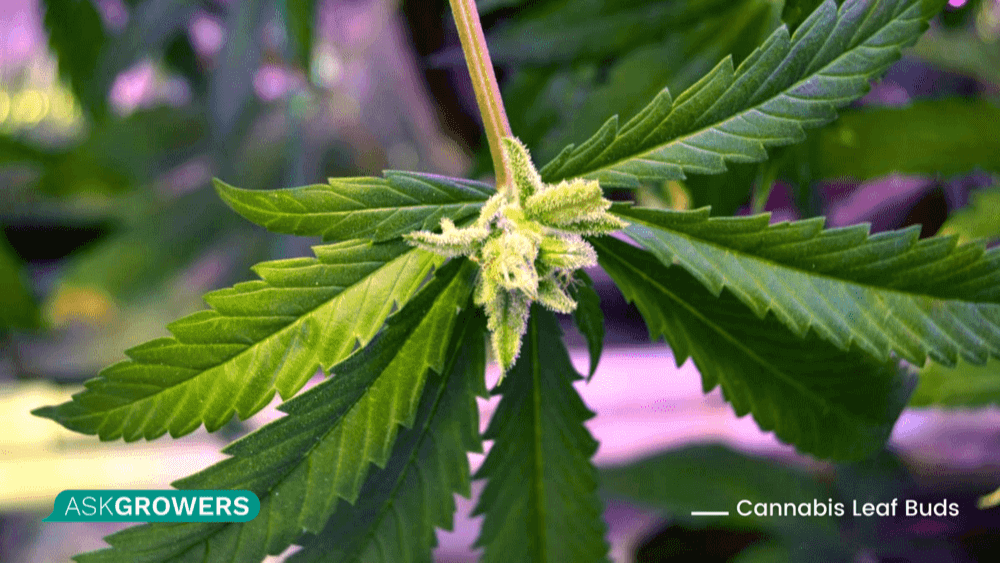
Cannabis Leaf Buds
Another popular mutation cannabis growers can face is the formation of leaf buds. This is the type of weed mutation that always dazzles the home grower. Leaf buds usually form at the base of the leaf, the place where the leaf and its stalk meet.
Just like with other mutations, this can be a fascinating change to see for a grower. However, this weed tends to have a poor yield. Some cultivators try to rescue the plant by removing leaf buds to allow leaf biochemistry to function alongside more normal lines. But in most cases, it doesn't work.

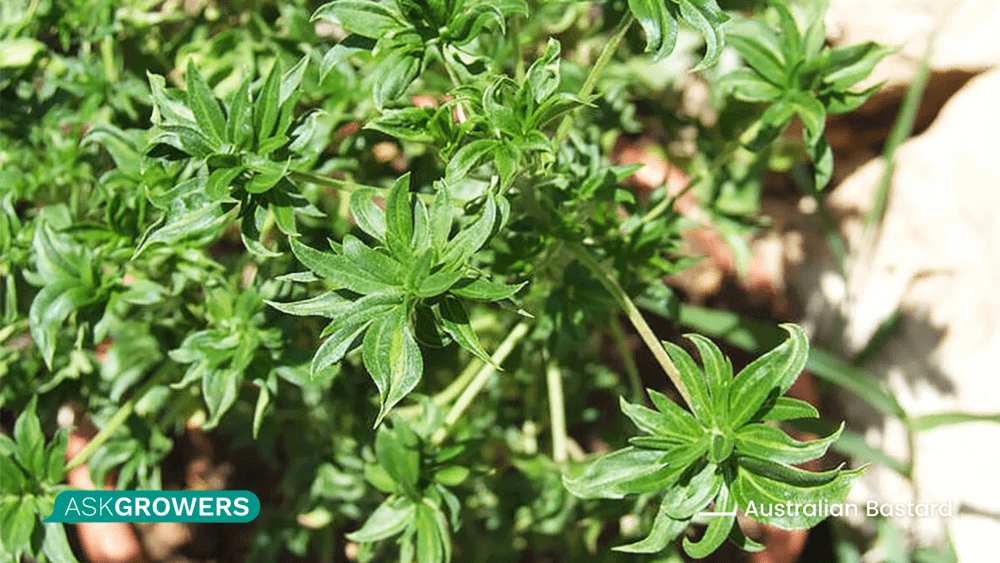
Australian Bastard
Australian bastard cannabis (also known as ABC) is a good example of how natural mutation happens and is used to improve the quality of cannabis for medical and recreational consumption. This mutation originated in Australia.
ABC started to make waves through breeding circles. The features of this weed, such as compact and stubby growth, a lack of serrated leaves, as well as an all-around vine-like appearance, made it a perfect choice for weed experiments for enhancement.
Such weed genetic mutations tends to have low THC levels. However, experienced growers looking for experiments can try to strengthen the THC level without losing its very covert-looking appearance. That is what started to happen when this mutation was unacknowledged and why it became so popular in the cannabis breeding world.

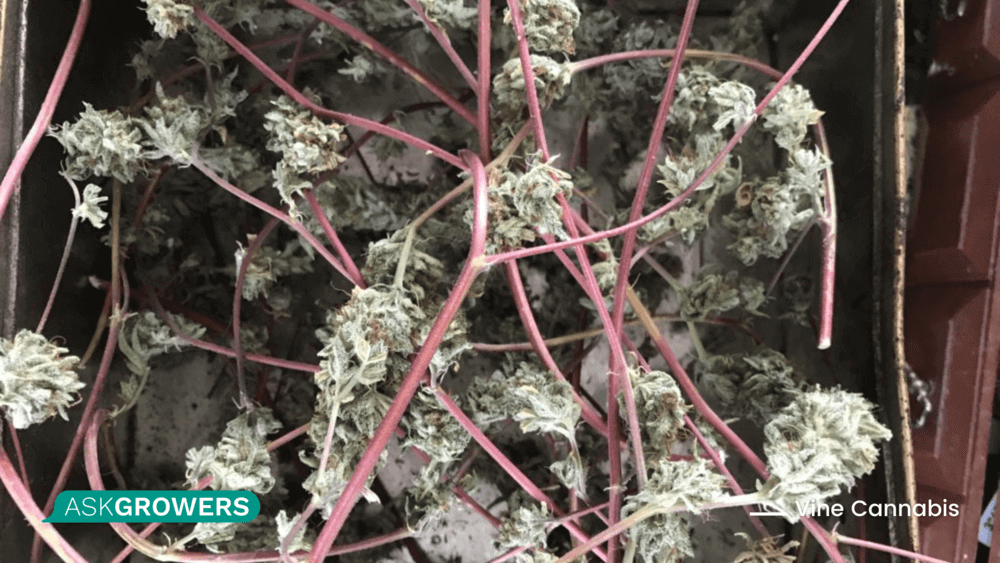
Vine Cannabis
Vine cannabis is a spin-off mutation of the ABC type we mentioned above. This is one of the rare bud mutations that usually occurs when it is crossed with a gene pool already containing another unnoticed mutation.
The resulting weed starts to grow similar to its close relative - the hop. The hop is a climbing plant and a part of the Cannabaceae family. Plants with vine mutation grow thinner, with elongated stems spiraling around each other.
In proper conditions, these plants can grow all the way to the top of the stem and then start to grow downward toward the ground. While this is definitely not regular cannabis, this mutation allows the vine weed to grow into an incredibly bushy and strong plant with a high yield.

Polyploidism
Polyploidy, also known as Polyploidysm mutation, is the scientific term used for weed plants that have extra-developed areas, or what is known as elephantiasis. Even unskilled growers will notice that the plants are much bigger overall than they should be. This mutation can't be passed to other plants, and it doesn't seem to survive when crossed with other strains. Although more research is required, there is anecdotal evidence that polyploid marijuana can lead to extremely large yields and high potency of harvested buds.
.png)
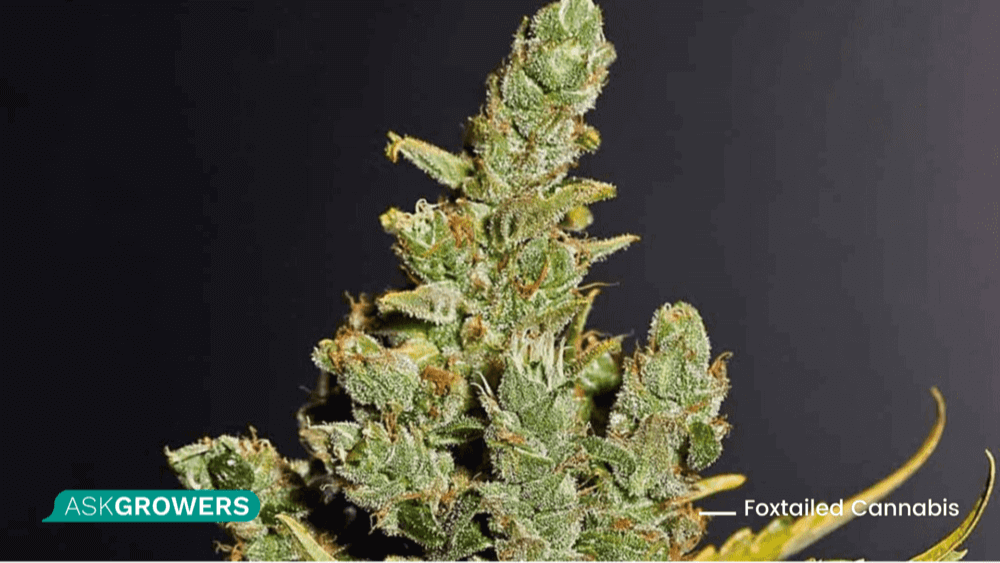
Foxtailed Cannabis
Foxtail is a mutation that can happen due to various reasons. In contrast to other types, this one can be the result of genetic mutations to improper growing conditions. Foxtail weed usually occurs when the plant experiences heat stress or bug attacks or when you give it nutrient boosters. Foxtails are noticeable because of their sudden spurts of growth on top of the bud that spirals outward. It is very typical for indoor-grown cannabis.
This mutation does not affect the quality of harvested buds, their effects, and taste. If this mutation comes from the genetic code of the weed, this phenotype tends to produce flimsy little plants with tiny bud sites. Some phosphorus-tolerant strains can also start foxtailing right after a PK boost during the mid–late vegetative stage.

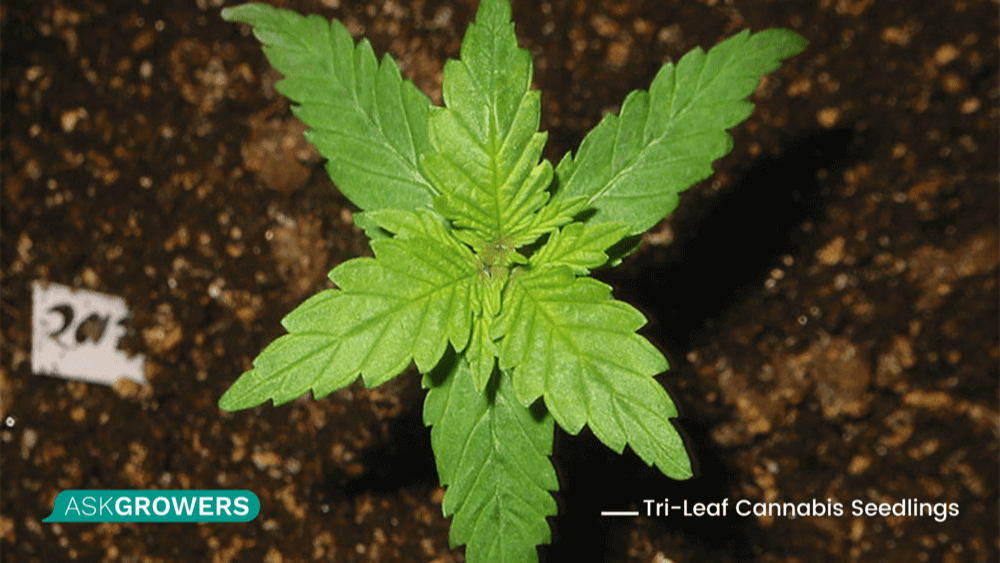
Tri-Leaf Cannabis Seedlings
Cannabis with this mutation produces three leaves instead of the two normal leaves. These seedings usually grow out of their tri-leaf tendencies since the plant ages during its bloom stage. Tri-leaf cannabis is also called a whorled phyllotaxy.
The 3 leaf Indica plants affected by mutation tend to be bushier than usual. Even new growers will see these changes at some point. In contrast to some mutations, this one doesn't offer any benefits, and it is more likely to be in the rank of most common weed plant deficiencies.

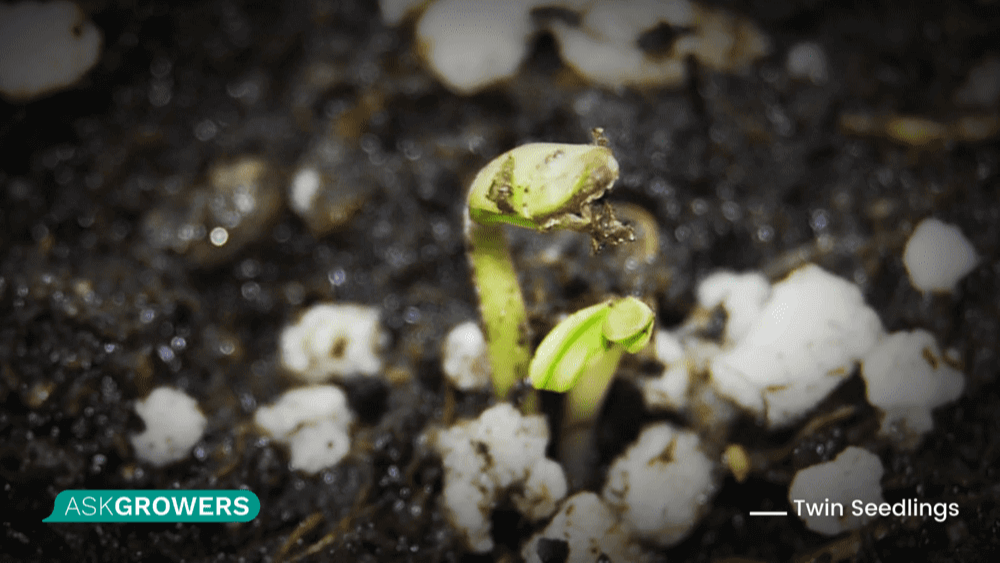
Twin Seedlings
This is a common mutation where polyembryonic seeds contain more than one seedling. When you germinate these seeds, they will develop two taproots instead of one. With proper knowledge and care, these seedlings can be successfully divided into two plants.
One of the resulting two plants will grow into a normal healthy offspring of both father and mother. The other one can become a descendant or a clone of the mother strain. These seeds do not offer any benefits for growers, so there is no interest in using them to breed cannabis.

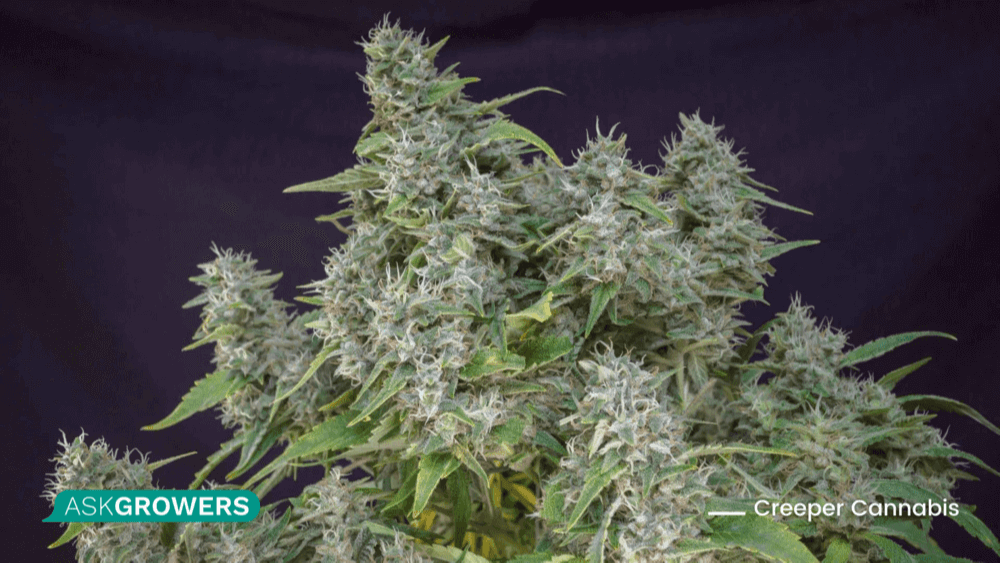
Creeper Cannabis
This cannabis is extremely huge, so its side branches are bowed all the way down to the ground to put roots again. This mutation usually happens with weeds growing in the wild tropic regions with high humidity levels and with certain Sativa strains that display this bizarre trait.
These plants grow extremely elongated stems that look similar to vines than normal cannabis stems. With time, the stems will put on weight, toppling over and eventually reaching the ground and starting to root out. Although there is small information regarding this mutation, it still attracts growers pruning to increase yield.

Marijuana Mutations | Final World
Cannabis plant flower mutations can be interesting to watch, but they do not bring any real benefits or opportunities for growers. In almost all cases, mutations affect the flower bud growth and quality. In contrast to diseases where the affected part of the weed is usually localized and can be trimmed so the rest of the plant remains safe, mutations are genetic, so they affect the entire plant.
While most mutations are in the DNA of the plant, some of them, like foxtail buds, can be worsened by stress or improper growing conditions. Gowers should watch out for their plants since some mutations may have a greater chance of causing hermaphroditism, so they could pollinate the rest of the garden and damage the harvest.
Luckily, most mutations can be easily noticed, so you can reduce these chances to zero for the rest of the crop. Buy cannabis seeds only from trusted seed banks and learn about growing weed 101 to make sure you get the healthy growing weed.
Read Also: Fluffy Buds? No Thanks: A Helpful Guide to Growing Dense and Sticky Cannabis

 Growing
Growing
 Guides
Guides



.png)



 (1).png)

.jpg)





Be the first and share your opinion
Write a Review