Everything You Need to Know About CBN

There are more than a hundred various cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. In recent years, THC and CBD have been in the spotlight and extensively studied and utilized due to their therapeutic properties, leaving behind CBN.
In fact, CBN was the first phytocannabinoid identified by scientists and isolated from hemp in 1896, but it didn’t receive much attention. What is CBN cannabinoid? This acronym stands for cannabinol and is considered a minor cannabinoid because it occurs at a low concentration and is difficult to isolate for medicinal purposes. In this post, let’s shed some light on this chemical that was undeservedly lost out of sight.
Read Also: What Are Cannabinoids, Their Types, and Effects?
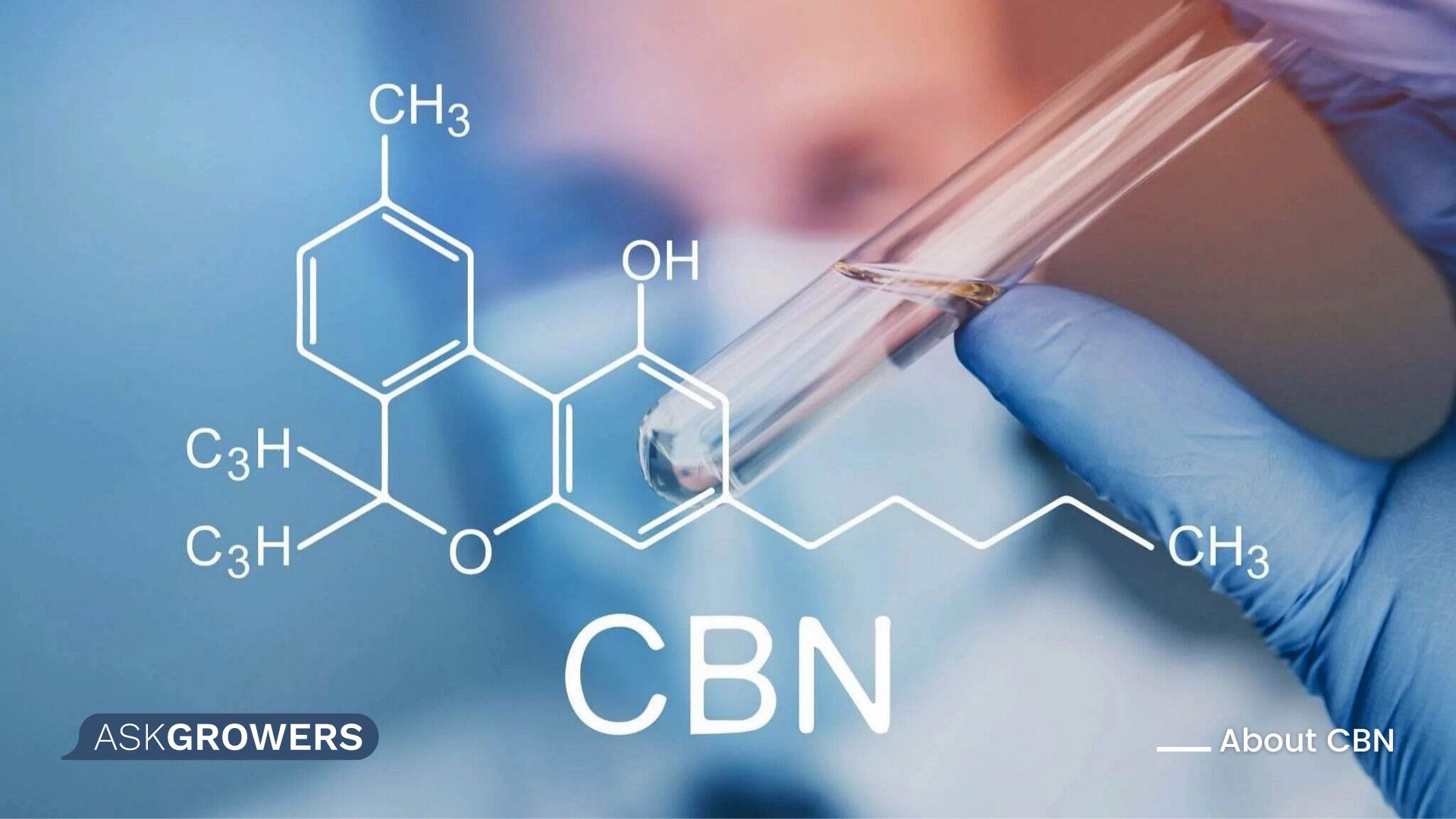

What Is CBN in Weed?
What is cannabinol? CBN cannabinoid doesn’t occur naturally. It is a product of oxidization found in aged and dry cannabis plants. It is formed after the plant is harvested. When THC is oxidized (exposed to heat, light, and oxygen), it turns into a unique metabolite with no psychoactive effects – CBN. It takes time for THC to degrade and convert to another chemical, creating an obstacle in getting a new compound. So, the cost of CBN can be up to 10 times higher than that of CBD.
This chemical is not widely available but can be found in several forms:
- CBN Oil
- Tinctures
- Capsules
- Isolate
- Vape pens
- Gummies
- Topicals
Consumers are more likely to find CBD products that include CBN than goods containing cannabinol exclusively.
Read Also: Introduction To Cannabinoids
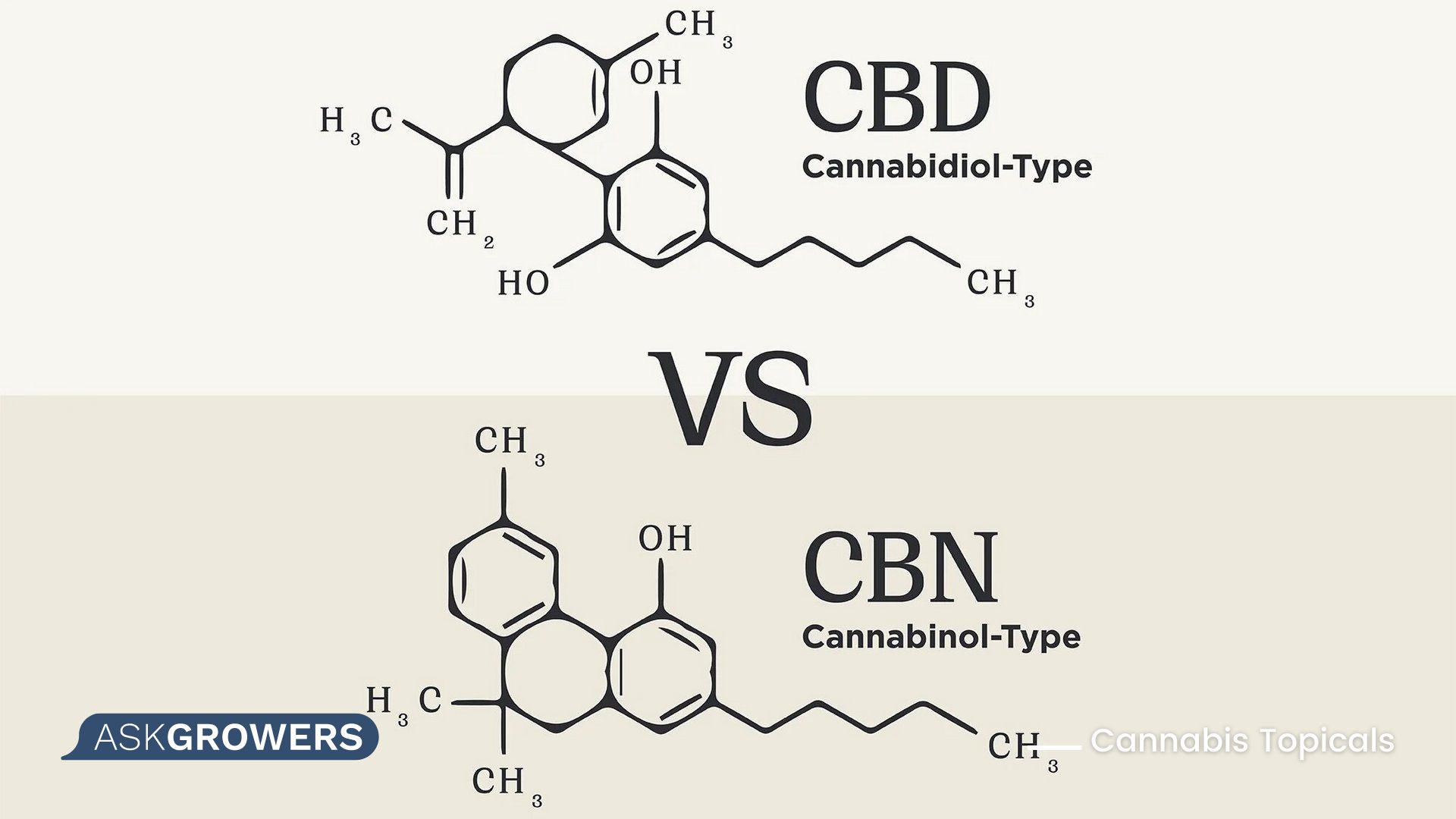
CBN vs CBD
CBD’s effects have been studied extensively, making it a popular compound in mainstream retail products. With little research, CBN is not so far-famed.
The origin of both components is different. CBD exists independently within the cannabis plant and is converted from cannabidiolic acid through heat. In addition, manufacturers can breed strains that contain a high CBD amount.
The production of CBN is more complicated. There are no plants that contain a high CBN level themselves. It is a result of oxidative processes within the plant. Cannabinol can be formed in different ways:
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin acid combined with heat converts into tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) and then into CBN;
- Over time, tetrahydrocannabivarin acid with no heat also turns into CBN;
- It can be synthesized for economic reasons to make the process less labor-intensive.
The amount of cannabinol depends on different factors, such as the THC level in weed flowers and their exposure to heat, light, and time.
What does CBN do? Regarding effects, CBN and CBD do share similarities by demonstrating anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, sleep-improving, and pain-relieving properties.
Unlike THC, they are considered mild drugs. It means they don’t alter one’s mind. CBD shows no intoxicating effects but can affect a cannabis high and prevent negative THC effects. When people use a lot of CBN, it can weaken or block THC effects.
Read Also: What is CBDV and How is It Different From CBD?
CBN vs THC
Actually, it’s hard to compare partially unknown CBN with such a heavyweight as THC. THC is well known for inducing high typically associated with weed consumption. Also, it helps improve sleep and mood, reduces pain, increases appetite, and offers other medicinal benefits.
As a derivative of THC, CBN may be technically viewed as its weaker version, which is 25% as effective as THC. Since cannabinol is not available in high amounts in cannabis products, there is no chance of its overconsumption. So, most experts treat it as a compound unable to cause strong psychoactive reactions.
Known to have a greater affinity for the CB2 receptors, cannabinol still acts on the CB1 receptors similar to THC. So, it shows some effects typical for THC and borrows some of its properties.
How Does It Work?
Cannabinoids interact within the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a major system in the human body that regulates numerous critical responses, such as immune response, metabolism, appetite, sleep, mood, memory, inter-cell communication, etc. ECS is composed of endocannabinoids naturally produced by the body and cannabinoid receptors. The most studied are cannabinoid receptors 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptors 2 (CB2). The CB1 receptors deal with pain perception, motor activity, and other central nervous system components registered in the brain. The CB2 receptors deal with the physical body and the peripheral nervous system – skin, bones, immune system, etc.
Cannabinoids bind and interact with these receptors, having a big impact on their effectiveness. THC and CBD connect to the CB1 receptors. The connection of CBN to the CB1 receptors is poor. It binds better to the CB2 receptors and deals more with the body than with the brain, particularly with cells related to the immune system. While studies are preliminary, other interactions within ECS haven’t been demonstrated well yet.
Read Also: CBC Cannabinoid (Cannabichromene): Benefits, Effects, Legal Status

Medical Properties of CBN
CBN effects are being studied for their positive impact on health and skin. The results are promising; however, research is scarce regarding human clinical trials. Preliminary studies suggest potential therapeutic benefits of CBN, such as:
- Sleep-inducing. Since THC is a well-known cannabinoid for sleep, cannabinol also demonstrates an ability to sedate and improve sleep quality as a byproduct of THC oxidation;
- Antioxidative. Due to this property, the chemical can neutralize free radicals in the body;
- Pain-relieving. The compound showed musculoskeletal pain mitigation in joints and decreased muscle sensitization;
- Neuroprotective. CBN provides relief for nerve pain and may delay the onset of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, as proven by a rodent study. It has the potential to reduce or prevent natural cell death;
- Antibacterial. Cannabinol can act as an antibacterial agent against some bacteria strains resistant to traditional antibiotics;
- Appetite-improving. Like THC, CBN can be an effective appetite stimulant, as shown in studies on rats;
- Anti-inflammatory. As an anti-inflammatory agent, cannabinol can potentially reduce rheumatoid arthritis and heal chronic wounds with concomitant inflammation;
- Anticonvulsant. Due to this property, the chemical mitigates symptoms of seizure disorders, including epilepsy.
In one study on rabbits, CBN was active in lowering intraocular pressure, which is associated with glaucoma. Also, this compound plays an increasing role in the wellness industry.
It is important to highlight that studies on humans are limited, so more research is needed to bolster these findings and get more consistent results.
Read Also: Americans With Disabilities Find New Relief and Freedom With Cannabis
CBN Benefits Over Other Cannabinoids
People with sleep disorders who are sensitive to THC should opt for CBN. Both compounds help establish a good sleep schedule and regulate circadian rhythms, but cannabinol is safer and carries no side effects. In comparison to CBD, CBN is also a preferred option to CBD for sleep.
The ability of cannabinol to target the CB2 receptors (while THC prefers the CB1 receptors) gives it better credibility in alleviating symptoms of autoimmune conditions, such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Only one CBD-based medicine approved by the FDA is used to treat seizures. Preliminary research shows that CBN could be more beneficial in treating seizures, provoking no negative reactions.
Read Also: What is CBG in Weed, and What Does It Do?
Side Effects and Potential Risks
CBN’s side effects are presently unclear because there is insufficient evidence of its long-term effects on human health. Usually, people turn to CBN products for assistance with relaxation and sleep, but these reactions may also be viewed as adverse. So, high doses of cannabinol can make consumers intensely sleepy, drowsy, and sedated. Especially when combined with CBD, CBN can cause extreme drowsiness, which is a possible risk for people who operate machinery or a motor vehicle.
CBN can also exhibit and increase the THC amount in one’s system leading to a positive drug test result, even if the THC level is undetectable.
Similar to other cannabinoids, cannabinol may interact with some prescription medications. To be safe, talk to a healthcare provider before using this chemical.
Conclusion
To date, cannabinol has not been studied to a much extent. The thing that sets this compound apart from other cannabinoids is its strong sedative ability. It is good at reducing anxiety with no side effects. Research on humans is lacking, but scientists will definitely find more uses for it.

 Guides
Guides

.png)
.png)



 (1).png)

.jpg)





Be the first and share your opinion
Write a Review